It happens to every one of us from time to time. When you try to visit a website to check your email, browse items or read a blog, you get a strange message called “400 Bad Request.” At the end, everything seems pointless, and you try to understand the problem.
Even though 400 Bad Request is one of the most common errors people see online, it is simple to overcome. In most cases, the website isn’t at fault; the error with connecting to the website occurs on your side, regardless of the browser you’re using.
We’ll go through the meaning of a 400 Bad Request and the reasons why it happens, along with sharing six methods to solve this issue in Google Chrome. It’s time to restore your internet browsing experience!
What does the term 400 Bad Request Mean?
Error 400 Bad Request meaning is that the server is unable or unwilling to fulfil the request sent by you. To put it briefly, what your browser sent was not understood by the server.
A website’s server accepts your browser’s request only if the request is assembled in a given way. If a request lacks some information, is no longer valid, or its files are unusually large, the server reports back with an error 400.
Many cases are caused by:
- Browsers that have caches or cookies filled with viruses
- An incorrect URL may result from improper syntax.
- The ability to upload big files.
- When the DNS lookup is incomplete.
- Problems caused by using browser extensions or below-standard programs
As a result, a 400 error occurs when the server struggles to comprehend the web request.
6 Steps to Handle the 400 Bad Request Error

Now that you understand what the 400 bad request meaning, we will discuss ways to solve the problem. Below, we have listed six proven ways to solve the issue.
1. Empty the Cache and Delete the Cookies
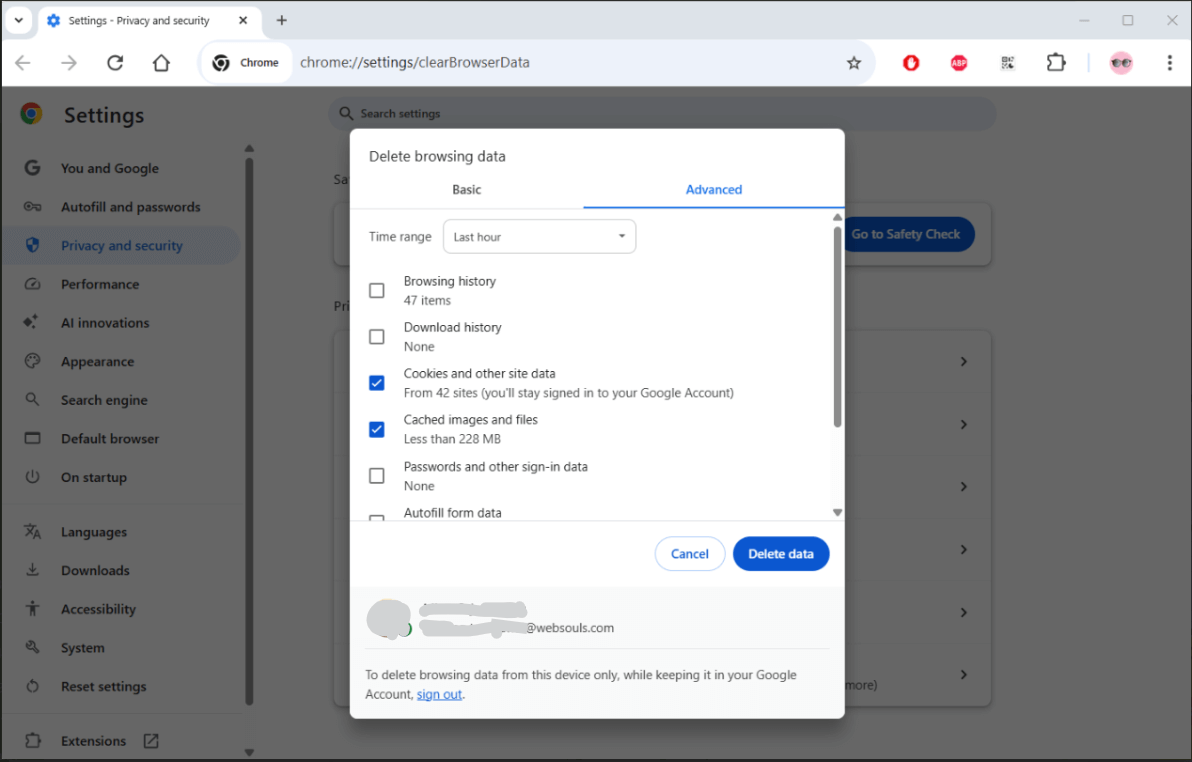
Using old cookies and cached files can often lead to a 400 error. Such files in your storage can disturb the process of speaking to the server by your browser.
How to fix 400 Bad Request on Google Chrome?
- Open Chrome.
- Click the icon with the three dots in the upper right area of the screen.
- Access Settings, proceed to Privacy and Security and then click Clear Browsing Data.
- Browse through Cookies as well as other site data and Cached images and files.
- Click on the Clear data option.
Afterwards, press F5 or click the refresh button to see if everything is fine.
2. Look for Any Errors in the URL
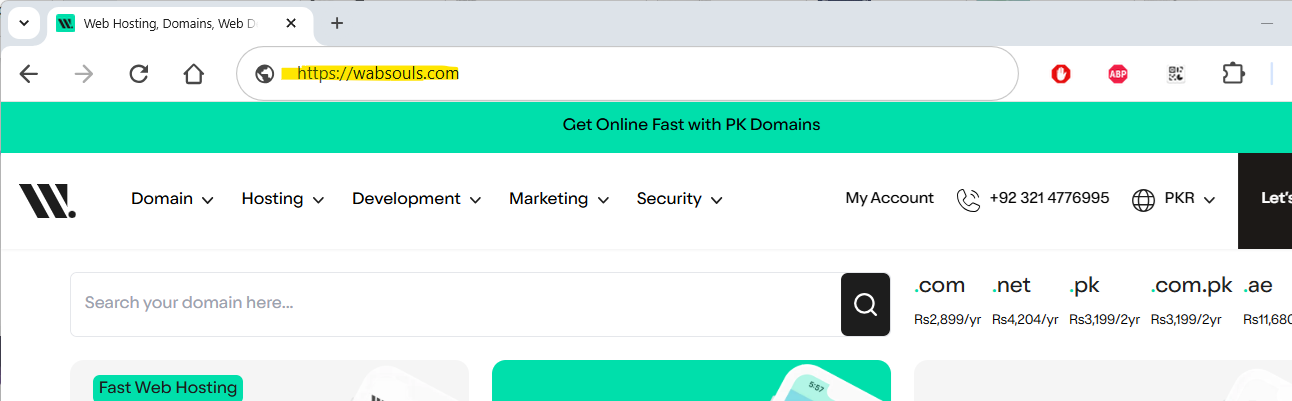
A 400 Bad Request can happen simply because someone entered the URL address incorrectly. Having too many characters, using the wrong code, or pasting code the wrong way can interrupt your server.
Tips:
- Check to see if there are any extra slashes, signs or extra questions at the end of the URL.
- Go to the homepage of the website instead of a direct link to the page.
- If the URL is not working, see if the simple base address works.
3. When Sending a Message, Use Smaller Files
There are servers out there that only allow the transfer of files that are very small. If your file is larger than the limits, you could get the 400 Bad Request error.
Solution:
- Don’t forget to compress the file.
- Upload your files in smaller sizes whenever you are able to.
- Look through the documentation online or call support to see what file size is allowed.
4. Remove the DNS cache memory
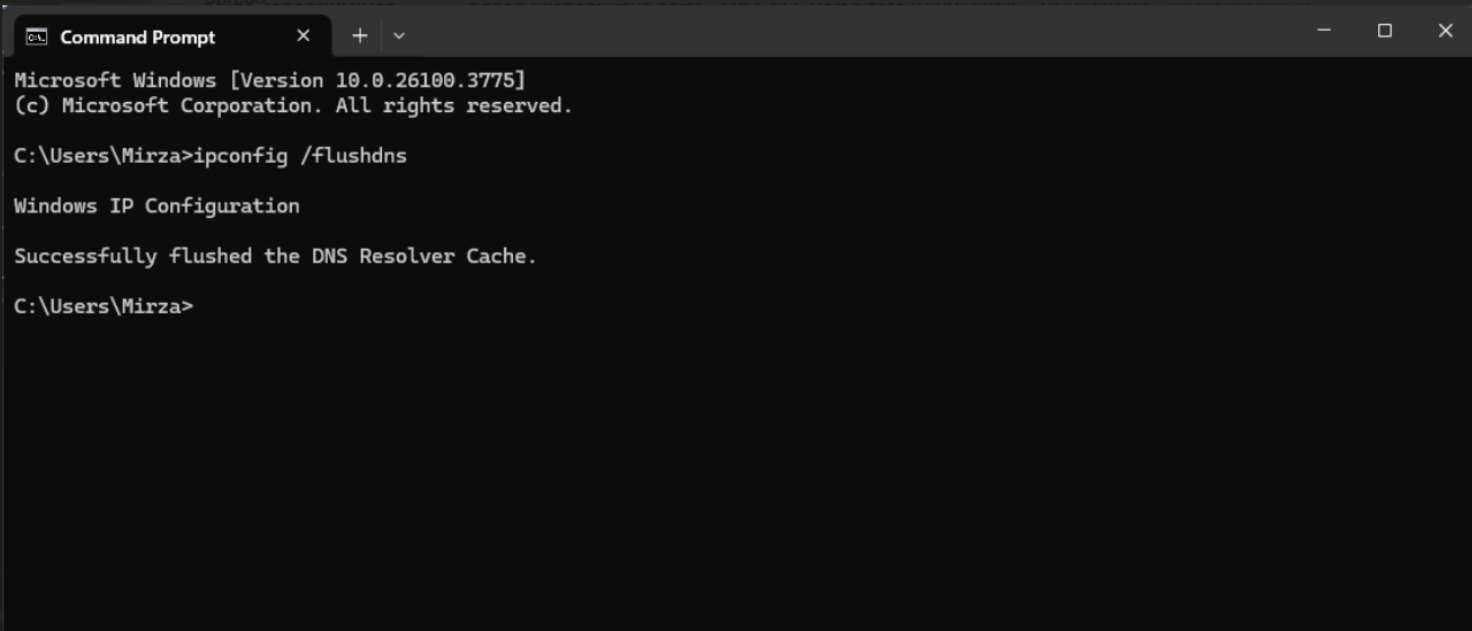
Broadly, a DNS problem can cause a 400 bad request when the existing data is either old or damaged.
Flushing the DNS on Windows:
- Access the Command Prompt in Administrator mode.
- Action: You have to type in
ipconfig /flushdns. - Press Enter.
By doing this, your DNS resolver cache is emptied, which could solve the problem.
5. Turn Off the Extensions
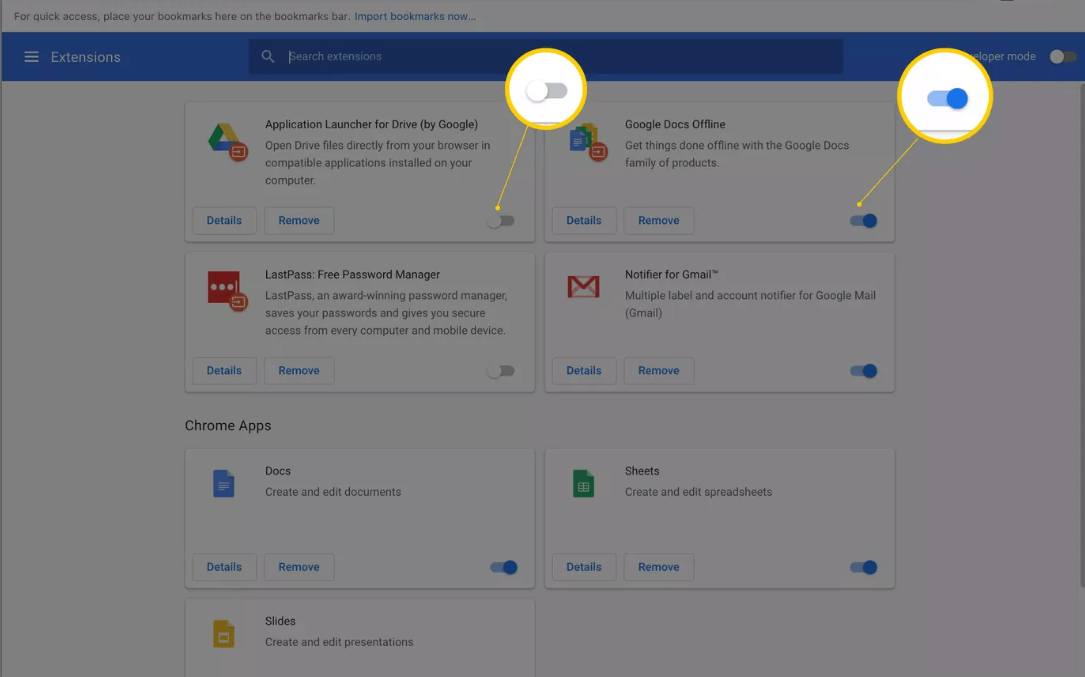
Setting up specific extensions on your browser can sometimes result in an error 400.
- Click on the three-dot menu at the top of Chrome.
- Select Extensions and then hit Manage Extensions.
- If something seems strange, choose and turn off any unnecessary extensions.
- Hit the refresh button and look for the error again.
Once the error does not occur, add extensions one at a time to see which is causing the problem.
6. Use A Different Internet Browser/Incognito Option
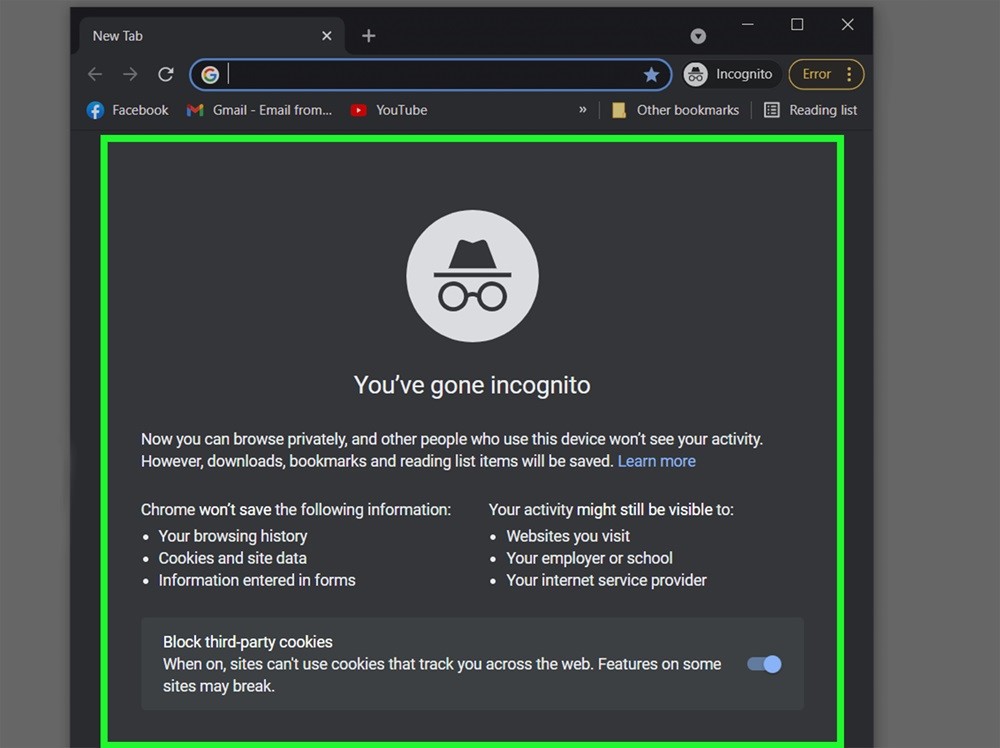
At times, problems with the browser or user preferences may disrupt requests to websites. By using either the Incognito option in Chrome or another browser, you can better identify the issue.
If you want to start Incognito Mode in Chrome, this is how:
Hit the Ctrl+Shift+N keys or select New Incognito Window from the menu with three dots.
If the problem is fixed in Incognito or a different browser, the culprit is likely one of your browser extensions, cookies or your cache.
To Wrap Up
Getting the 400 Bad Request error is annoying. However, it’s simple to resolve in most cases. Making a request over the Internet involves cookies, URLs or DNS, and by clearing them or checking their information, you can resolve 400 errors on any browser.
After figuring out the 400 Bad Request meaning and using the provided guides, you will easily handle the error and keep browsing.
Has this type of issue happened in your browser recently? Feel free to share your questions, and Websouls will explain how to resolve those as well.