Key Takeaways:
- Slow DNS lookup can significantly impact website loading times and user experience, increasing bounce rates and lowering conversion rates.
- DNS resolution delays typically add 20–120 milliseconds to load times, but optimizing DNS performance can reduce this considerably.
- Using fast DNS providers like Cloudflare, Google DNS, or Amazon Route 53 can significantly speed up DNS resolution.
- Caching DNS queries and simplifying DNS records are effective strategies for reducing lookup time.
- Regular DNS performance monitoring helps identify and fix issues early, ensuring optimal website speed and performance.
Slow DNS lookup is often the culprit behind slow-loading webpages, frustrating users and impacting website performance. As online services become more essential, optimizing DNS resolution is crucial. DNS delays can add 20-120 milliseconds to load times, and even a slight slowdown can increase bounce rates and reduce conversions. The good thing is that these issues can usually be fixed with simple changes. In this guide, we'll explain the causes of slow DNS lookups and share actionable solutions to improve performance.
What is DNS?
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is a system that converts human-readable domain names into IP addresses, allowing browsers to load websites. For example, when you type in www.google.com, DNS translates it into a numerical IP address like 216.58.217.14. This way, your browser knows where to find the website.
How Does DNS Work?

The DNS system works by following a simple process:
- User Request: You type a website address (URL) into your browser.
- DNS Query: The browser sends a DNS query to a DNS server, asking for the IP address of the domain.
- DNS Lookup: The DNS server checks its records and sends the IP address back to the browser.
- Website Load: Once the browser receives the IP address, it connects to the server and loads the website.
The time it takes for this process to complete is called DNS lookup time. A delay in any of these steps can lead to slower website load times.
What Causes Slow DNS Lookup?
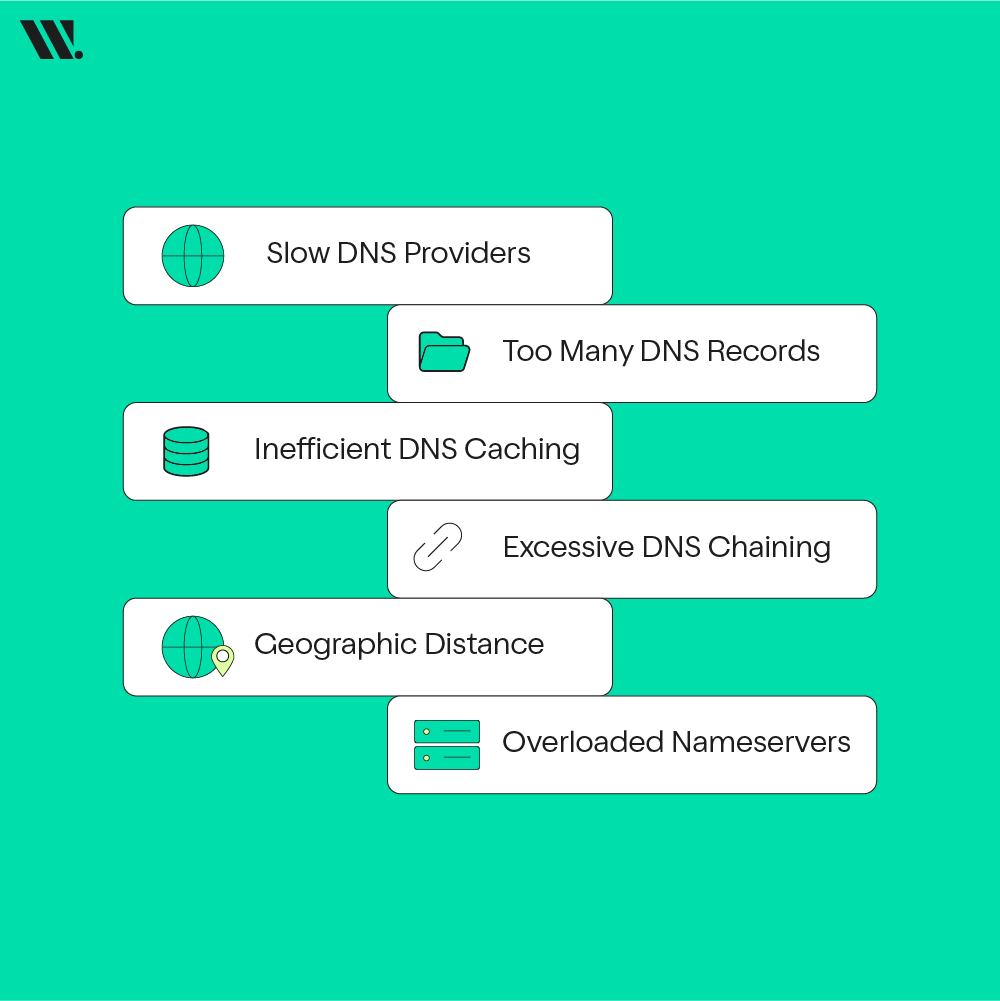
Several factors can slow down the DNS resolution process, making websites take longer to load. These include:
- Slow DNS Providers: Default DNS servers from ISPs or hosting companies can be slower than alternatives.
- Too Many DNS Records: A website with a lot of DNS records can result in longer lookups.
- Inefficient DNS Caching: Without caching, the same DNS queries may be repeated multiple times, leading to delays.
- Excessive DNS Chaining: Multiple redirects (like CNAME records) can slow down the resolution process.
- Geographic Distance: The farther away the DNS server is from you, the longer it takes to resolve the query.
- Overloaded Nameservers: Slow nameservers at your web hosting provider can cause DNS delays.
How to Fix Slow DNS Lookup?
_1767282464.png)
Improving DNS lookup times can significantly reduce website loading times and improve user experience. Here’s how you can address slow DNS resolution issues:
1. Use a Fast & Reliable DNS Provider
Most ISPs provide default DNS servers that are often slower than third-party services. Switching to a faster and more reliable DNS provider can reduce lookup times. Some well-known DNS services include:
- WebSouls DNS: Offers reliable and fast DNS services with optimized performance for local and global users. Its infrastructure ensures faster lookups and minimal downtime.
- Cloudflare DNS: Known for its speed and security. Cloudflare DNS offers a 1.1.1.1 service, which is one of the fastest DNS resolvers globally.
- Google Public DNS: Google offers a fast DNS service (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) that prioritizes speed and security.
- Amazon Route 53: A highly scalable DNS service that can handle large traffic loads and reduce DNS resolution time.
These providers often have better infrastructure and more global coverage, resulting in faster DNS lookup times.
2. Reduce DNS Records
Having too many DNS records can slow down the lookup process. If your website has unused or outdated DNS records, they can add unnecessary complexity to the resolution process. Here's what you can do:
- Remove unused records: Regularly check and delete DNS records that are no longer needed (such as old A, CNAME, or TXT records).
- Simplify your DNS structure: Avoid adding unnecessary DNS records. Each DNS query adds overhead.
- Avoid unnecessary redirects: Excessive CNAME redirects can cause delays. For example, instead of using multiple CNAME records (CNAME → CNAME → A record), point your domain directly to the final IP address.
3. Enable DNS Caching
DNS caching allows your browser and DNS resolver to store the IP addresses of websites for a certain period of time. This means that the next time you visit the same website, the DNS lookup will be much faster because the IP address is already cached.
- Browser Caching: Modern browsers automatically cache DNS results. Ensure that your browser is set to retain these records.
- Server-Side Caching: If you run a website, configure your server to cache DNS queries to avoid performing lookups for the same domain repeatedly.
- Operating System Cache: On servers, enable OS-level DNS caching to speed up lookups for frequently accessed domains.
By caching DNS results, you reduce the need for repetitive lookups and speed up the process.
4. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN is a network of servers that deliver web content to users based on their geographic location. CDNs help speed up website loading times by reducing the distance between users and the servers that store the website’s content.
- CDN DNS Resolution: Many CDNs, like Cloudflare and Akamai, have their own DNS infrastructure, which speeds up the DNS lookup process by serving users from the nearest available server.
- Reduced Latency: By using a CDN, DNS queries are resolved closer to the user, which reduces latency.
Popular CDN providers like Cloudflare or Akamai improve DNS resolution and content delivery speed.
5. Lower DNS TTL (Time to Live)
TTL is the time period for which DNS records are cached. By lowering TTL, DNS servers will refresh their records more often, which helps resolve new or updated DNS queries faster.
- Optimal TTL Range: A TTL of 300–600 seconds (5–10 minutes) is recommended for better performance, especially for websites that undergo frequent changes.
- Avoid High TTL: Setting a TTL value too high (such as 86400 seconds or 24 hours) can delay DNS updates and slow down the resolution process when changes occur.
Lower TTL values allow for quicker updates and faster resolution.
6. Avoid DNS Chain Lookups
DNS chaining occurs when a DNS query is redirected multiple times from one CNAME record to another, and eventually to an A record. Each additional redirect increases DNS lookup time.
- Point directly to IP addresses: Instead of chaining CNAME records (CNAME → CNAME → A record), point your domain directly to the A record that resolves to the IP address. This reduces the number of lookups.
Minimizing the number of redirects in your DNS structure can significantly reduce lookup time.
7. Check Hosting Nameserver Performance
If your hosting provider’s nameservers are slow or unreliable, this will increase DNS lookup time for your website. Here's what you can do:
- Test DNS Response Time: Use online tools like DNSPerf to check the DNS response time of your hosting provider.
- Switch Nameservers: If your hosting provider’s nameservers are slow, consider switching to faster third-party DNS services like Cloudflare, Google, or Amazon Route 53.
- Separate DNS and Hosting: If possible, use a separate provider for DNS management instead of relying on your hosting company. This can improve DNS performance and ensure that both services are optimized.
8. Enable HTTP/3 & QUIC (If Available)
HTTP/3 and QUIC are modern protocols that reduce connection overhead and speed up website loading. These protocols can also improve DNS resolution speed, especially when used with services like Cloudflare.
- What is HTTP/3 & QUIC? These protocols are designed to minimize delays during the connection process, including DNS resolution. They reduce packet loss and improve overall performance.
- Availability: If your CDN or hosting provider supports HTTP/3 or QUIC, make sure it is enabled to improve both website loading times and DNS resolution.
9. Monitor DNS Performance Regularly
DNS issues can sometimes go unnoticed, affecting the performance of your website over time. Regular monitoring helps identify problems early and allows you to fix them before they impact users.
- Track DNS Response Time: Use monitoring tools like Pingdom or DNSPerf to keep an eye on DNS response times and identify slowdowns.
- Look for Failed Lookups: Track failed DNS queries, which may indicate issues with your DNS server or configuration.
- Check Propagation Delays: Make sure your DNS changes propagate quickly across the internet, especially after updates to your DNS records.
If DNS still won’t work or is unresponsive, read our detailed guide on how to fix DNS Server not Responding and solve the issue effectively.
| Cause | Solution | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Slow DNS Provider | Switch to faster DNS providers like WebSouls, Cloudflare, Google, or Amazon Route 53 | WebSouls DNS |
| Too Many DNS Records | Remove unused records and simplify the DNS configuration | DNSPerf |
| Lack of DNS Caching | Enable DNS caching at the browser, operating system, and server level | Pingdom |
| Multiple DNS Redirects | Avoid chaining multiple CNAME records | DNSPerf |
| High TTL | Set DNS TTL values between 300–600 seconds for better performance | — |
| Slow Hosting Nameservers | Move to optimized custom nameservers or third-party DNS services | DNSPerf |
| No CDN | Implement a CDN to speed up DNS resolution and global delivery | Cloudflare |
Conclusion
Slow DNS lookup time and poor DNS resolution affect how fast websites start loading. With better DNS providers, optimized configuration, caching, and regular monitoring, you can cut DNS delays and improve performance. These steps help ensure users get faster access, which leads to a smoother browsing experience every time.
Need Help with DNS Optimization?
If you’re looking for reliable DNS management and fast performance, we offer optimized DNS services to improve your website’s speed and availability.
Contact us today to get started!
FAQs for how to fix slow DNS lookup
How can I check if my DNS is slow?
Use the dig command or tools like DNSPerf to measure lookup times; over 50ms indicates slowness.
Can caching improve DNS lookup speed?
Yes, local and recursive caching skips full lookups for repeat queries.
What is TTL, and how does it affect DNS speed?
TTL dictates cache duration; higher values (e.g., 3600s) speed up stable records by reducing queries.
Should I avoid multiple CNAME records?
Yes, CNAME chains add extra lookups, slowing resolution; use A records instead.
Can a CDN help with DNS resolution?
Yes, CDNs like Cloudflare use Anycast for faster global routing.
How often should I monitor DNS performance?
Weekly or post-changes, via DNSPerf for latency trends.
Will slow DNS affect SEO?
Yes, it delays loads, affecting Core Web Vitals and rankings.
Can modern protocols like HTTP/3 help DNS speed?
Indirectly via QUIC efficiency; combine with DoH for best results.