Key Takeaways
- JavaScript makes websites interactive, but it can hide content from search engines if not handled correctly.
- Google renders JavaScript using an up-to-date Chrome engine, but heavy scripts or dynamic content can delay indexing.
- Using server-side rendering (SSR) or pre-rendering makes sure that Google sees the full content quickly.
- SEO tools like URL Inspection, Lighthouse, and Screaming Frog help identify JS rendering issues.
- Common mistakes include blocked JS files, large scripts, missing canonical tags, and improper lazy loading.
JavaScript is used on almost every modern website. It adds interactivity through live forms, sliders, popups, and content that updates without a full page refresh. This makes websites feel fast and engaging for users. But search engines like Google must read and understand the final content to show your site in search results. Google has improved its ability to handle JavaScript, but many sites still face visibility issues if JS is not optimized.
Over 98% of websites use JavaScript today, showing how important it is. In Pakistan, online businesses are increasingly relying on frameworks like React, Vue, or Next.js for dynamic websites, booking systems, and interactive blogs. If Google cannot see key content because of JavaScript, your pages may not rank well, resulting in lower traffic. Proper JavaScript SEO helps assure that your site is visible, user-friendly, and ranks effectively.
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a programming language that runs in your browser. It allows web pages to update content dynamically without refreshing the page, making sites interactive and responsive.
- It handles user interactions, such as clicks, typing, or form submissions, in real-time.
- It can update page content, like showing new products in a shopping cart or live chat messages.
- JavaScript works with HTML and CSS to create fully interactive applications, almost like mobile apps inside a browser.
What is JavaScript SEO?
JavaScript SEO helps search engines to see and index content created or modified with JavaScript. Traditional SEO only reads static HTML. But JavaScript often loads content dynamically, so proper SEO ensures Google sees the final page. Good practices include testing rendering, using the right framework setup, and avoiding blocking sensitive scripts.
What is JavaScript Rendering?
JavaScript rendering is the process of executing code to display the full page. When a search engine crawls a site, it first reads the raw HTML. Then Google executes JavaScript to see the dynamic content. This is why JS-heavy pages may appear blank in source view but contain full content once rendered. Proper rendering allows Google to index the actual information users see.
How Does JavaScript Impact SEO?

JavaScript can improve or harm SEO depending on usage. It allows interactive and modern experiences, but can delay content visibility for search engines.
● Positive Impact
Interactive features keep users engaged longer, improving engagement metrics like dwell time and lower bounce rates.
● Negative Impact
Content loaded only after JS execution might be missed or indexed late, reducing visibility.
● Indexing Delays
Google queues JS pages for rendering, which can delay indexing for new or old pages.
● Crawl Budget Usage
Heavy or poorly optimized JS consumes more crawling resources, potentially limiting page coverage on larger websites.
How Search Engines Render JavaScript?
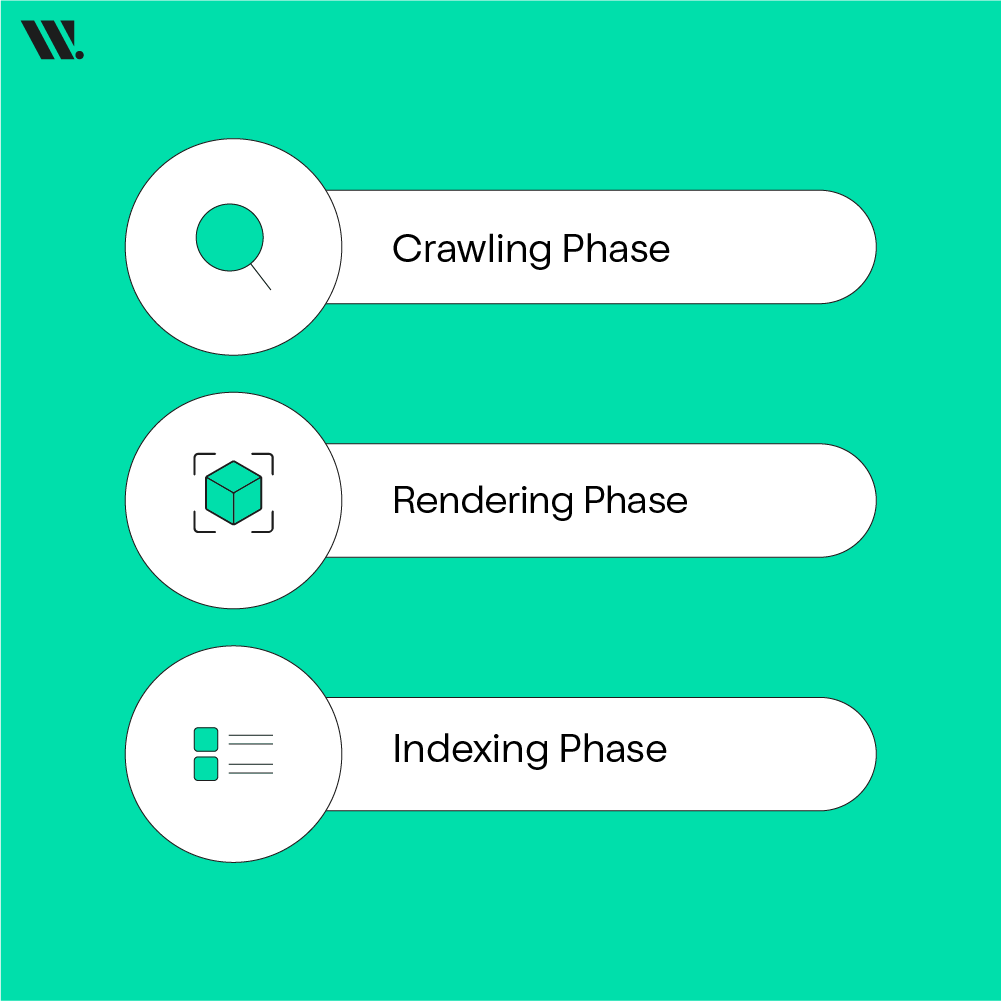
Google handles JavaScript in multiple steps: crawling, rendering, and indexing.
- Crawling Phase → Googlebot fetches raw HTML and linked resources. If JS or CSS is blocked, rendering fails.
- Rendering Phase → Google executes JavaScript in a headless Chrome browser, often with minor delays for complex scripts.
- Indexing Phase → Google reads the fully rendered HTML, including JS-modified content, links, and structured data.
View Source vs Inspect Element
The View Source shows raw HTML from the server before JS runs. Inspect Element displays the live DOM after JavaScript changes it. For SEO, the rendered view is closer to what Google sees.
| Feature | View Source | Inspect Element |
| Shows original HTML | Raw server content | Shows live content after JS |
| Includes JS changes | Not included | Fully rendered DOM |
| SEO relevance | Partial view | Closer to Googlebot’s view |
| Access | Right-click > View Page Source | Right-click > Inspect Element |
| Use for SEO check | Quick static check | Check rendered content |
Benefits of JavaScript for SEO and Users

When implemented correctly, JavaScript offers major advantages for both SEO and user experience.
- Better User Engagement: Infinite scrolling, filters, and interactive forms keep visitors on the site longer.
- Dynamic Content Updates: Personalization, live pricing, or product recommendations display relevant information to users instantly.
- Modern Features Without Reloads: Single-page apps load content fast, improving Core Web Vitals and user satisfaction.
- Mobile-Friendly Experiences: JS-powered responsive design ensures mobile-first indexing success.
- Rich Structured Data: JSON-LD or schema markup added via JS can create rich results in search, like star ratings or prices.
Common Errors / Challenges with JavaScript SEO
Many sites run into trouble because JavaScript hides content or slows down page performance. Google has improved its ability to render JS, but mistakes still cause lost traffic, poor rankings, and frustrated users. Sites that depend heavily on JS without optimization often struggle with indexing and visibility. Even if the content looks perfect to visitors, Google may not see it correctly if scripts are blocked or mismanaged. This is why understanding how JS affects SEO is essential for every website owner.
JS can cause problems if mismanaged:
- Resources blocked in robots.txt prevent Google from rendering pages correctly.
- Heavy JS bundles slow execution and waste crawl budget.
- SPAs with soft 404s return 200 status but show errors to users and bots.
- Inconsistent canonical tags confuse Google about which version to index.
Other common issues include scripts that load too late, broken dynamic links, improper lazy loading, and hidden content behind tabs or sliders. Even minor mistakes in JavaScript can make important information invisible to search engines, affecting rankings and traffic. Testing pages with tools like Google Search Console or Lighthouse can help identify these errors early.
How to Optimize JavaScript for SEO?

Optimizing JavaScript for SEO makes sure that your content is both visible to search engines and user-friendly. If done right, JavaScript can improve user engagement and performance while keeping your website accessible for search engines like Google. Here are key optimization techniques to ensure your site ranks well and is correctly indexed:
1. Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) is one of the most effective ways to optimize JavaScript for SEO. With SSR, the server sends fully-rendered HTML pages to the browser, which means that Googlebot sees the complete content right away, without having to wait for JavaScript to execute.
How it works: When a user requests a page, the server processes the content, runs the JavaScript, and delivers the final HTML to the browser. This eliminates the need for Google to wait for the JS code to run before seeing the content.
Benefits: It helps search engines index the content immediately, improving visibility and reducing crawl delays.
Examples: Popular frameworks like Next.js and Nuxt.js offer server-side rendering out of the box, making them great choices for SEO-friendly websites. These frameworks are particularly helpful for single-page applications (SPAs), where content is dynamically loaded.
2. Pre-rendering / Static Generation
Pre-rendering or static generation involves generating the final HTML of the page at build time, rather than dynamically generating it when the page is requested. This is particularly useful for websites with consistent content, like blogs or product pages.
How it works: Tools like Gatsby, Hugo, or Jekyll can generate static HTML files from your dynamic JavaScript code. These pre-built pages are then served to both users and Googlebot.
Benefits: It speeds up the rendering process since the HTML is already prepared, and Google can crawl and index the content instantly. Static generation is especially useful for content-heavy websites where new content is added regularly but doesn't require real-time dynamic changes.
Example: For a blog built with Gatsby, the website would generate static HTML pages for each blog post. Googlebot sees this content without needing to wait for JavaScript to load, and users can access the content faster as well.
3. Minimize & Defer JavaScript
Large JavaScript files can slow down your site, especially if they are blocking the page from loading. Minimizing and deferring JavaScript is important for improving your site’s speed and overall SEO.
How it works:
Minimize JS: This involves removing unnecessary characters, whitespace, and comments from the JavaScript code. Minified code is smaller and loads faster, which is important for both SEO and user experience.
Defer JS: Deferring non-essential JavaScript allows the HTML to load first. Non-critical scripts, such as analytics or tracking scripts, can be deferred to load after the main content is ready.
Benefits:
Faster page load times: Google uses page speed as a ranking factor, so minimizing JS improves your SEO.
Reduced rendering time: By deferring non-critical scripts, you make sure the page renders faster, keeping users engaged.
Example: By using the async or defer attributes in the script tag, you can tell the browser to load JavaScript after the main HTML content has finished loading. This ensures that the core content is available to both users and search engines quickly.
4. Lazy Loading of Images and Videos
Lazy loading is a technique that delays the loading of images or videos until they are needed, i.e., when they are about to be viewed by the user. It’s particularly important for JavaScript-heavy websites with lots of images, such as e-commerce stores or blogs with media-rich content.
How it works: Instead of loading all images or videos when the page first loads, lazy loading only loads them when the user scrolls near them. This reduces initial page load time and improves the overall user experience.
Benefits:
- Improves page load time, which impacts SEO positively.
- Reduces unnecessary resource consumption, especially on mobile devices with limited data and processing power.
Example: Implementing lazy loading on an online store’s product images helps ensure that only the visible products are loaded at first. As the user scrolls down, additional images are loaded.
5. Use Structured Data for Rich Results
JavaScript can also be used to implement structured data (like JSON-LD), which allows search engines to better understand the content of your site and display it in rich results (like star ratings, product prices, or event times) on search results pages.
How it works: JSON-LD can be added to the JavaScript code of your website, providing search engines with detailed information about the content. This improves the visibility of your content in search results with improved features.
Benefits:
- Rich results improve CTR (Click-Through Rates) by making your content stand out in search results.
- Provides more context to search engines, helping them index your content more accurately.
Example: A local Pakistani restaurant can use JSON-LD to mark up its menu items, pricing, and reviews. This makes it more likely that Google will display a rich snippet with star ratings and other relevant information in the search results.
Tools and Techniques for JavaScript SEO Audits
To ensure that JavaScript websites are optimized for search engines, it's important to use the right tools for auditing and testing. These tools can help identify JavaScript rendering issues, crawl errors, and any other SEO-related concerns that could affect a website's visibility and performance. With JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js, it’s essential to use the appropriate tools for a comprehensive audit. Here are some of the recommended tools and their primary uses for auditing JavaScript SEO:
| Tool Category | Recommended Tools | Primary Use in JS SEO Audit |
| Search Engine Tools | Google Search Console | Check for crawl errors, mobile usability, index coverage, and use the URL Inspection Tool to see how Googlebot renders a specific page. |
| Performance Audits | PageSpeed Insights | Analyze performance metrics (Core Web Vitals), identify render-blocking scripts, and get actionable speed improvement suggestions. |
| Structured Data Validation | Rich Results Test | Validate that structured data (Schema markup), often implemented with JavaScript, is correct and available to Google. |
| Site Crawlers | Screaming Frog SEO Spider | A desktop-based crawler that can be configured to render JavaScript, allowing you to identify issues like broken links, missing meta tags, or JS redirects in the rendered DOM. |
| Ahrefs / Semrush / Sitebulb | Enterprise-level cloud crawlers offering comprehensive site audits with JavaScript rendering capabilities and visual reports to identify issues at scale. | |
| Browser Extensions & DevTools | Chrome DevTools | Manually debug by disabling JavaScript locally, analyzing network requests, checking performance in the "Performance" tab, and viewing code coverage. |
| View Rendered Source (Extension) | Compares the raw HTML with the fully rendered HTML (after JavaScript execution) side-by-side, highlighting differences. | |
| Tech Stack Analysis | Wappalyzer / BuiltWith | Identify the website's underlying tech stack and JavaScript frameworks (e.g., React, Angular) to personalize your audit approach. |
When JavaScript is Deployed Without SEO Planning
When a JavaScript framework is launched without any SEO planning, search engines may struggle to see and index the website’s content. Pages often load as empty shells because important text, links, and metadata appear only after JavaScript runs. This can lead to slow or incomplete indexing, weak rankings, and low organic traffic. New pages may take weeks to appear in search results, and some may never rank at all. For businesses, this means lost visibility, fewer visitors, and missed growth opportunities, even if the site looks perfect to users.
Common JavaScript SEO Myths
JavaScript SEO is often misunderstood, which leads to fear, confusion, and poor technical decisions. Many of these myths come from old information, back when search engines struggled to process JavaScript. Today, Google has improved a lot, but JavaScript still needs a proper setup to work well with SEO. Understanding the facts helps teams build modern websites without affecting search visibility.
Myth: Google cannot index JavaScript
Fact: Google can index JavaScript by rendering pages using an up-to-date Chrome browser. If content is accessible after rendering, Google can read and index it.
Myth: Client-side rendered sites cannot rank
Fact: Client-side rendered (CSR) sites can rank, but they often face slower indexing. Using server-side rendering or pre-rendering improves reliability and speed.
Myth: JavaScript always slows down SEO
Fact: JavaScript only causes issues when it is heavy or poorly optimized. Clean, well-structured JS can support fast and SEO-friendly websites.
Myth: View Page Source shows what Google sees
Fact: View Page Source only shows raw HTML. Google looks at the rendered page after JavaScript runs, which is closer to what Inspect Element shows.
Myth: Lazy loading always affects SEO
Fact: Lazy loading works well when implemented correctly. Content that loads as users scroll can still be indexed if it is accessible to Googlebot.
Understanding these myths and facts helps teams make smarter choices, avoid outdated fears, and build JavaScript websites that perform well for both users and search engines.
Final Thought
JavaScript creates interactive, modern websites, but SEO requires careful planning. Understanding how Google crawls JavaScript, testing with proper tools, and optimizing rendering help your site be visible and rank well.
If you need help auditing or optimizing your JavaScript site, WebSouls offers SEO solutions in Pakistan and globally, along with a free consultation to guide your next steps.
FAQs for JavaScript SEO
How does JavaScript affect website loading?
JavaScript can delay page loading because browsers must download and run scripts before showing content. Heavy or unoptimized JS can slow both user experience and search engine rendering.
Can Google index JavaScript websites?
Yes, Google can index JavaScript websites by rendering pages using a modern Chrome browser. Content must be accessible after rendering for proper indexing.
What is the difference between CSR and SSR for SEO?
CSR loads content in the browser after JavaScript runs, which can delay indexing. SSR sends complete HTML from the server, allowing Google to see content immediately.
What is two-wave indexing in Google?
Google first indexes the raw HTML of a page, then renders JavaScript later to index dynamic content. This second wave can be delayed for complex pages.
What is the difference between “View Source” and “Inspect Element”?
View Source shows the original HTML sent by the server, while Inspect Element shows the page after JavaScript has modified it.
What is the hydration concept in JavaScript websites?
Hydration is when JavaScript adds interactivity to HTML already rendered on the page. It connects static content with live JavaScript behavior.
What is Static Site Generation (SSG)?
SSG creates fully built HTML pages at build time instead of on request. These pages load fast and are easy for search engines to index.
Can Google see content hidden behind user interactions like tabs or buttons?
Yes, Google can index hidden content if it is present in the HTML after rendering. Content loaded only after the user clicks may not be indexed.